Author: Brooke Carmen, PT, DPT: Doctor of Physical Therapy and Blog Contributor. Loves fun informational gems. Fitness addict and wannabe foodie. Emphasizes patient-specific treatment style and promotes goal-oriented care. Learn more about Brooke on here.
When I was in middle school, I was screened yearly for scoliosis in gym class. It was a terrifying day when we would have to stand in front of the nurses in a sports bra, bend forward to touch our toes, then stand up and wait patiently to hear our results. I remember standing there, freezing, blankly waiting for my diagnosis, terrified that I may have some sort of disease in my back. That’s not really the case.
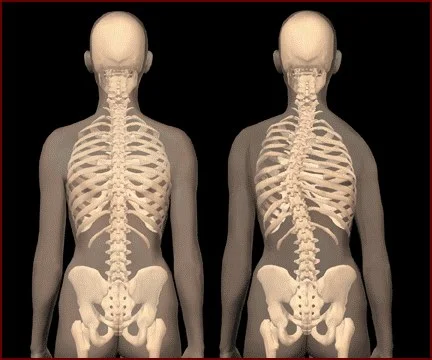
SCOLIOSIS is a condition when the spine is curved side-ways, mainly visible in the frontal plane (your view when you stand facing the mirror, the front of your body being reflected). There is a rotational component to scoliosis as well, usually going in the opposite direction of the curve in the mirror view. Scoliosis is not to be confused with KYPHOSIS which is visible in the sagittal plane (your view when you stand at a 90 deg. angle to the mirror, the side of your body being reflected).
The nurses were looking for something called an “ADAM’S SIGN” or “Forward Bend Test.” When bending forward, if you can see a hump on your back (right or left), it can be indicative of spinal malalignment. It is one sign of scoliosis, but it does not mean you absolutely have scoliosis. To know, you would need an x-ray. Even if you suspect you have scoliosis, though, you don’t need to expose yourself to radiation right away. That would be indicated if your mid to low back pain started to impact your daily activities and your doctor suspected a scoliotic curve that may need to be addressed outside of just conservative care.
There are four main different types of scoliosis: CONGENITAL, NEUROMUSCULAR, DEGENERATIVE, and IDIOPATHIC. The word “congenital” means you were born with it. Neuromuscular scoliosis is from an abnormality of muscles and nerves in your body. You see this with a diagnosis like cerebral palsy or spina bifida, both diagnoses that you would be well aware of at this point in time if you had them. Degenerative scoliosis is caused by trauma or something like osteoporosis (the thinning of your bones). I mostly come across idiopathic scoliosis, a type of scoliosis that has no direct cause. It is thought to be inherited, but no one knows for sure.
So what do people with scoliosis do when they have it? Depending on the severity, scoliosis can be treated either CONSERVATIVELY (non-surgically) or NON-CONSERVATIVELY (surgically). Something like physical therapy is conservative. Physical therapy combines different types of exercises to try and slow the aggressiveness of the curvature. We also look at things like flexibility and joint motions to make sure you’re able to maintain as much motion as you can. In some cases, we could recommend brace use. An example of a non-conservative treatment is a spinal fusion. A spinal fusion is when hooks, wires, screws, etc. are placed in the spine to combine segments and promote straighter alignment. This is in more severe, aggressive cases of scoliosis (most commonly neurologic in nature).
If you have misalignment of your back or suspected abnormal posture with back pain, it wouldn’t hurt to get screened for scoliosis or other causes of pathological neck, thoracic (rib cage region), and low back symptoms. Shoot me or my coworkers an email or call our clinic to see if you are appropriate for screening.
Terminology Review:
SCOLIOSIS: An abnormal curvature of the spine that involves abnormal in the frontal plane with a rotational component
KYPHOSIS: An abnormal curvature of the spine that involves abnormal alignment in the sagittal plane, usually without a rotational component. Most commonly seen with postural weakness. “Hunchbacked.”
ADAM’S SIGN: A test to check for potential scoliosis. Also known as the “Forward Bend Test.” The person bends forward, stopping midway. If a “bump” is present on the right or left in their thoracic region (rib cage area), scoliosis may be present.
FRONTAL PLANE: An anatomical plane. Also known as the coronal plane. Your view when you stand directly in front of a mirror.
SAGITTAL PLANE: An anatomical plane. Your view when you stand side ways to a mirror.
CONGENITAL: Something that is usually present at birth, whether it be a disease of physical misalignment. A type of scoliosis.
NEUROMUSCULAR: Anything related to the nerves and muscles in your body. A type of scoliosis.
DEGENERATIVE: A progressive condition over time that may or may not lead to loss of function. A type of scoliosis.
IDIOPATHIC: A condition that has no definitive cause. A type of scoliosis.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT: Non-surgical. Physical therapy, chiropractic care, acupuncture, and massage therapy are examples.
NON-CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT: Surgical. A spinal fusion, total knee replacement, or injection are one of many examples.